Harnessing the power of compound exercises can transform your fitness routine into a powerhouse of efficiency and effectiveness.
Story Snapshot
- Compound exercises maximize workout effectiveness and efficiency.
- Scientific evidence supports multi-joint movements for health benefits.
- Experts recommend targeting all major muscle groups twice weekly.
- Strength training is crucial for reducing chronic disease risks.
The Evolution of Strength Training
Strength training, once reserved for athletes, has evolved into a crucial component of general health guidelines. The American College of Sports Medicine and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health emphasize its importance for all adults. Since 2002, national health organizations have formally recommended resistance training, highlighting its role in enhancing health and performance. The rise of sedentary lifestyles has further underscored the need for accessible and efficient training methods.
Recent research has shifted focus from aerobic exercise to strength training’s benefits. Meta-analyses between 2018 and 2022 show that even a modest amount of strength training can significantly reduce mortality risk. As our understanding of exercise physiology improves, compound exercises have emerged as the gold standard for maximizing results in minimal time.
Understanding Compound Exercises
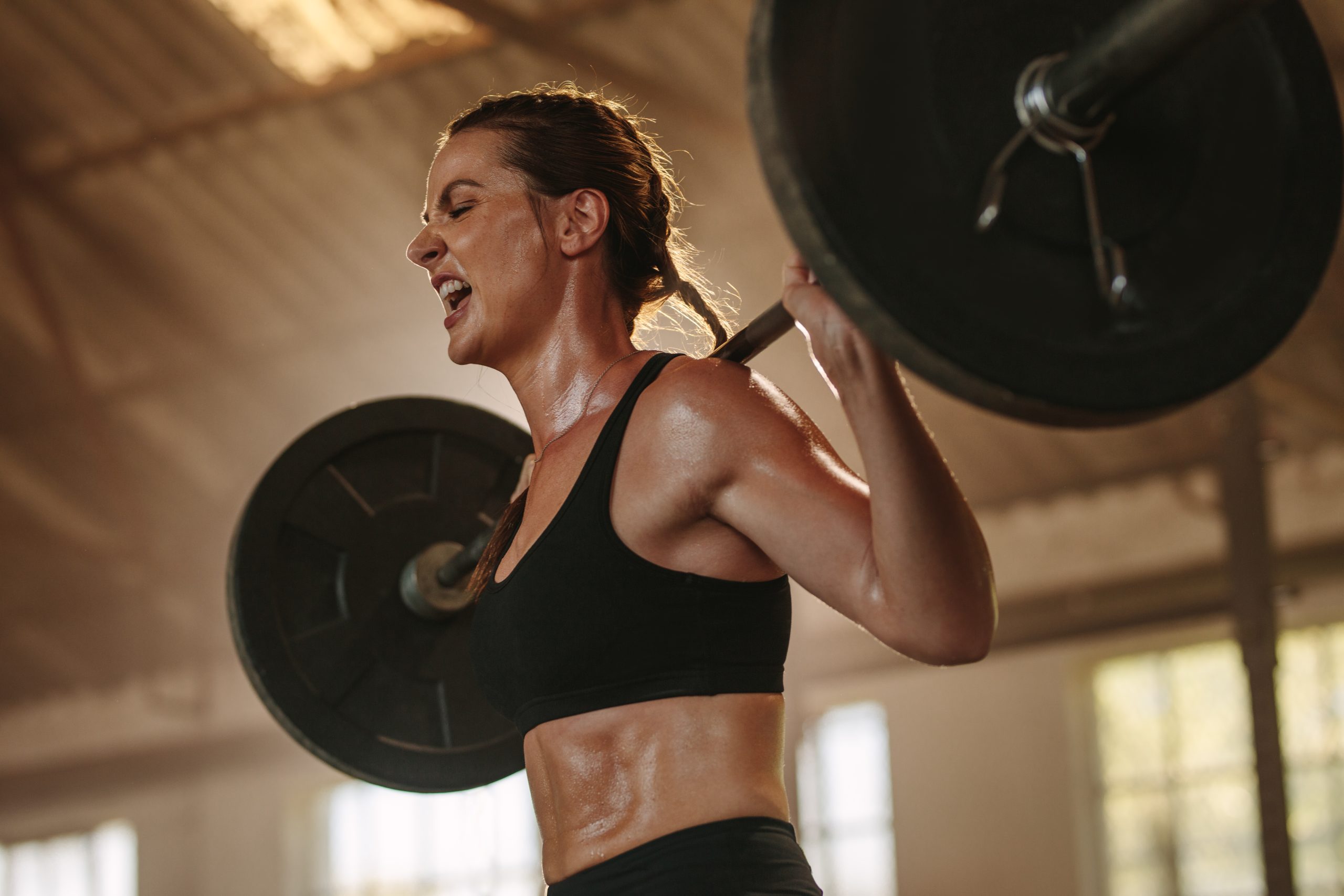
Compound exercises involve multiple joints and muscle groups, offering a time-efficient way to build strength and muscle mass. Movements like squats, deadlifts, and bench presses are staples in any effective workout regimen. These exercises not only engage major muscle groups but also improve functional capacity and metabolic health. Experts recommend incorporating these into routines at least twice weekly to target all major muscle groups effectively.
Unilateral exercises, such as split squats and single-arm presses, enhance core stability and activation, providing additional benefits when equipment is limited. While bilateral exercises are more efficient, unilateral ones can supplement for targeted muscle development or rehabilitation.
Guidelines for Effective Strength Training
To optimize results, experts suggest performing 6–12 repetitions per exercise, with 1–2 sets per muscle group, using 70–85% of one-rep max. This structure ensures both strength and muscle hypertrophy. Contrary to past beliefs, more is not necessarily better; 30–60 minutes of strength training per week yields substantial health benefits. The key is consistency and proper exercise selection, especially for older adults and those at risk for chronic diseases.
Supervision by qualified professionals is critical for safety and effectiveness. Individualized program design ensures that exercises meet personal goals and abilities, reducing injury risk and enhancing outcomes.
The Impact of Strength Training
Strength training’s benefits extend beyond the gym. Short-term, it improves muscle strength and functional capacity. Long-term, it reduces risks of cardiovascular disease, cancer, diabetes, and premature mortality. Societally, it promises enhanced quality of life, reduced healthcare costs, and greater independence for older adults. As the fitness industry shifts towards evidence-based programming, demand for qualified trainers and accessible resources grows.
The consensus among experts is clear: compound exercises are essential for achieving health and fitness goals efficiently. By incorporating these into regular routines, individuals can harness the full potential of strength training, reaping benefits that extend far beyond physical appearance.
Sources:
Iversen, V.M. et al. (2021). “No Time to Lift? Designing Time-Efficient Training…” PMC.
Harvard Health Publishing (2019). “Resistance training by the numbers.”
Kraemer, W.J. et al. (2002). “Resistance training for health and performance.” PubMed.
Mayo Clinic. “Strength training: Get stronger, leaner, healthier.”