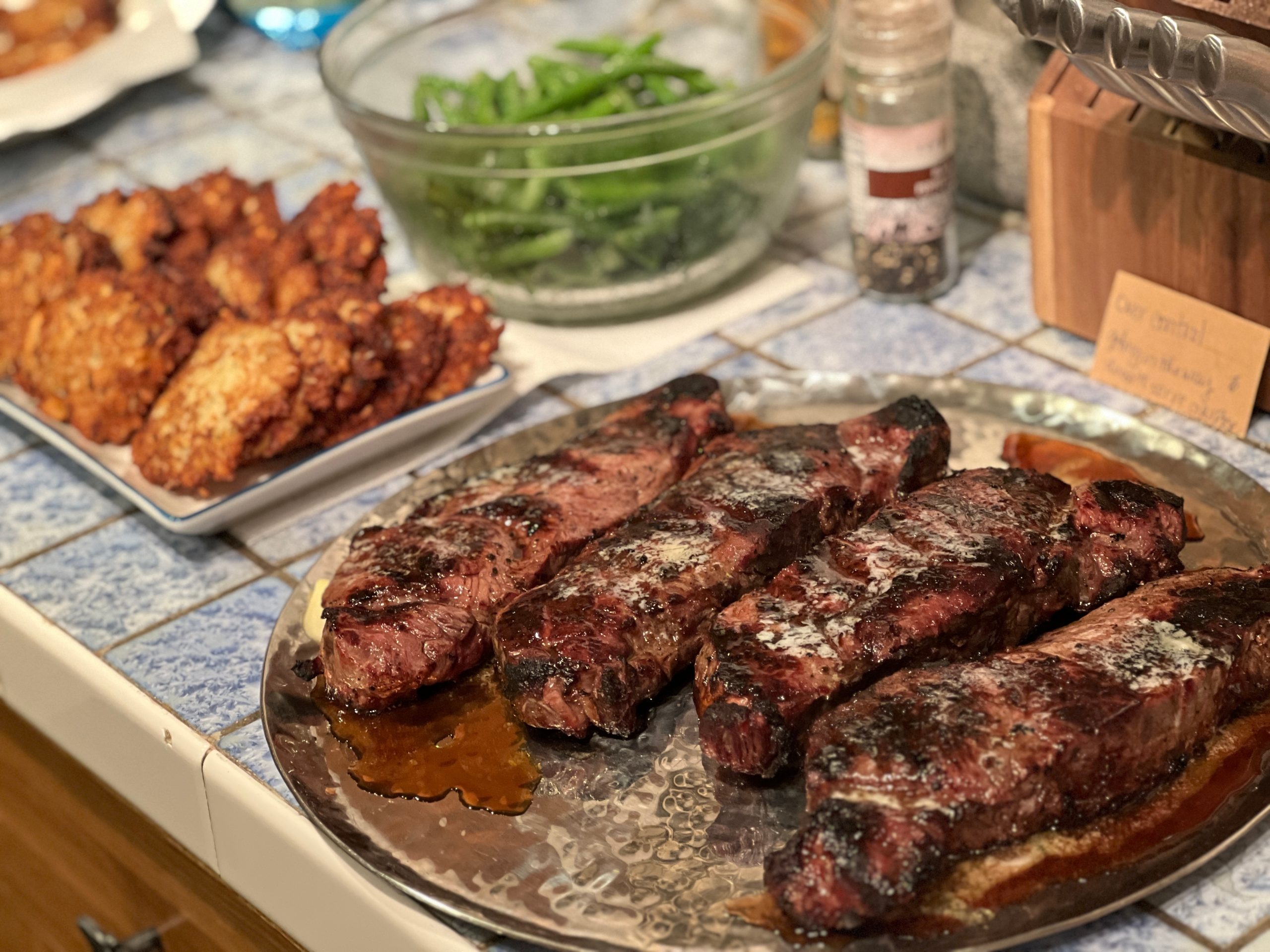The return of meat to the diet is more than a culinary change—it’s a personal and scientific journey that reflects evolving nutritional needs.
Story Overview
- Individuals are reconsidering plant-based diets due to health and nutritional needs.
- Recent studies suggest meat can be part of a healthy, balanced diet.
- Debates continue on meat’s role in nutrition amidst changing guidelines.
- Scientific findings emphasize the importance of context in dietary choices.
Reintroducing Meat: A Shift in Dietary Choices
In recent years, a notable shift has occurred as many individuals who once adopted vegetarian or plant-based diets are reconsidering their choices. This change is largely motivated by evolving nutritional needs and the latest scientific findings on the role of meat in human diets. As people age and their health status changes, they often find that reintroducing meat can address specific nutritional requirements, especially for those at risk of deficiencies like iron and B12.
How To Prepare Your Body To Eat Meat Again (If It's Been A While) https://t.co/jQx7gDxdL3
— Consciousness Intervention (@CSIntervention) August 17, 2025
Health professionals and scientists increasingly discuss the nuanced impacts of meat consumption. Recent studies from 2022 to 2025 highlight that moderate meat intake, particularly when focusing on lean and unprocessed options, can be compatible with longevity and health. This insight is reshaping debates that previously leaned heavily towards plant-based diets as the sole path to health.
The Science Behind Meat Consumption
Research has shown that while excessive consumption of red and processed meats is linked to chronic diseases like cardiovascular disease and cancer, moderate consumption of unprocessed meats can offer nutritional benefits. These include complete proteins and essential vitamins critical for various populations, such as the elderly and pregnant women. The ongoing debate is not just about whether to consume meat, but how much and what type to include in a balanced diet.
Studies emphasize the importance of personalized nutrition, taking into account age, health status, and lifestyle. As dietary guidelines evolve, they increasingly reflect the complexity of individual nutritional needs, moving away from one-size-fits-all recommendations.
Impact on Society and Industry
The reintroduction of meat into diets has broader implications beyond individual health. Economically, it affects demand within the meat and alternative protein markets. Socially, it fuels debates about diet and identity, while politically, it may influence public health policies and dietary guidelines. Nutritional science’s growing recognition of context in dietary advice marks a significant shift in how nutritional information is communicated and applied in public health.
The food industry is also seeing changes, with increased focus on sustainable and ethical meat production. The rise of “flexitarian” diets, which incorporate both plant-based and animal-based foods, highlights the industry’s need to adapt to changing consumer preferences and scientific insights.
Sources:
Total meat intake is associated with life expectancy