A middle-aged woman collapses in a grocery store after dismissing weeks of fever and a mysterious rash, only to discover she was battling a potentially fatal tick-borne illness that could have been treated with early intervention.
At a Glance
- Tick-borne illnesses can cause serious health complications if symptoms are ignored, with Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever being the most lethal in the U.S.
- Common symptoms include fever, rash, muscle pain, and fatigue, which may appear days to weeks after a bite
- Ticks prefer hidden areas like sock bands and waistbands, making bites easy to miss
- Immediate tick removal and seeking medical attention for symptoms are crucial preventive measures
- Most tick-borne illnesses are bacterial and treatable with antibiotics if caught early
The Stealthy Threat of Tick Bites
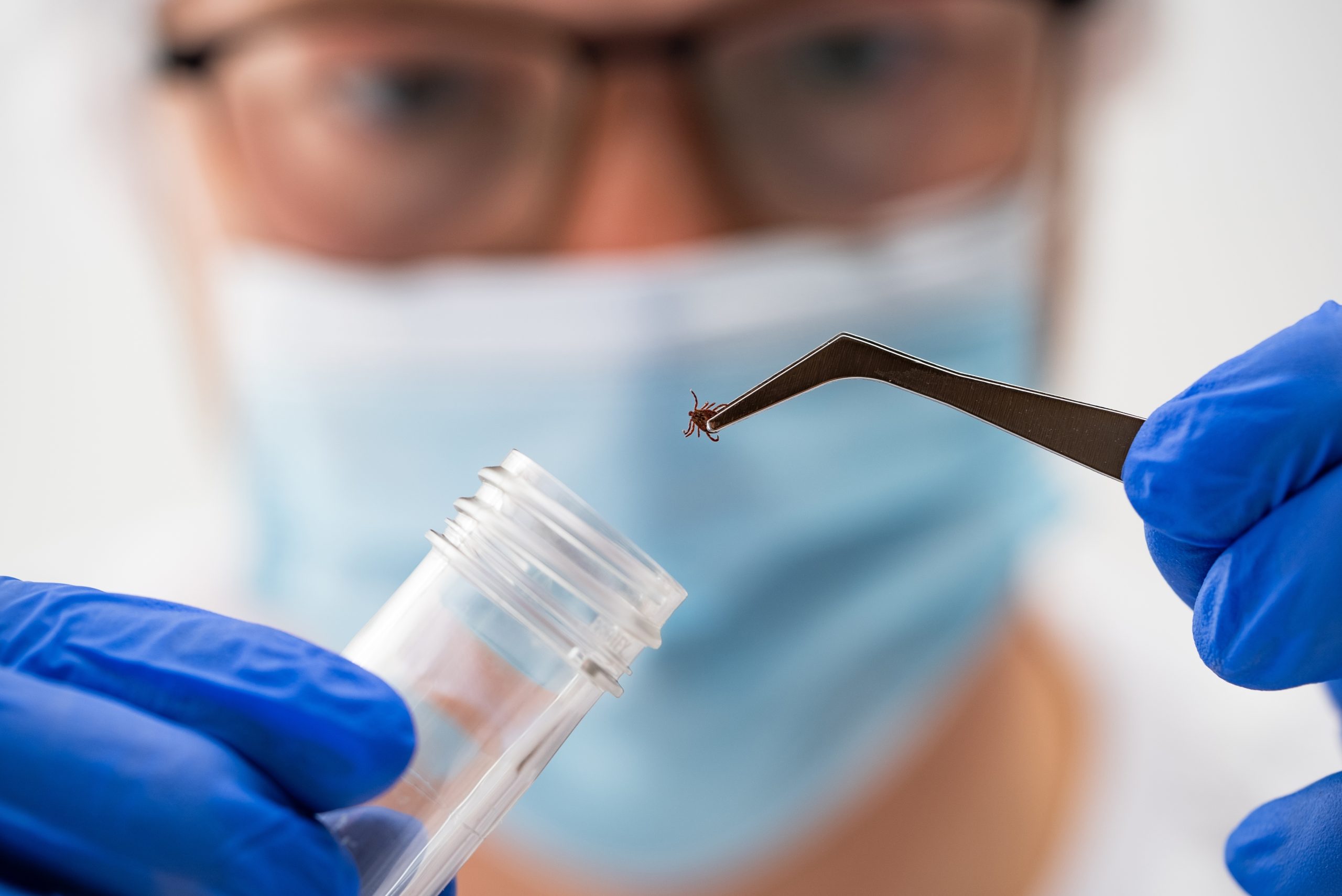
Ticks pose a silent health threat that many adults overlook until serious symptoms develop. These small arachnids often bite without detection, preferring concealed areas of the body where they can feed undisturbed. “Ticks are a little bit sneaky. They like your sock bands, waistbands and other areas where you have a lot of hair; so you can be bitten and not even know it,” explains Dr. Kayla Stover, a specialist cited in research from the University of Mississippi Medical Center.
Most active during summer months when outdoor activities increase, ticks detect potential hosts through breath, body odors, heat, moisture, and vibrations. Once attached, they can remain feeding for days, increasing the risk of disease transmission. Hard ticks, which are more common in many regions including Mississippi, typically attach for extended periods, while preparing to feed can take anywhere from 10 minutes to 2 hours.
Dangerous Diseases Transmitted by Ticks
While tick bites themselves may cause only minor irritation, the diseases they transmit can be severe or even life-threatening if left untreated. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF) represents one of the most serious threats in many southern states. “You can’t play around with that Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever,” warns Dr. Jerome Goddard, emphasizing the urgency of treatment for this potentially fatal condition that presents with fever, headache, and a distinctive rash.
Lyme disease, while less common in some southern regions, remains a significant concern for travelers and in endemic areas across the northeastern United States. Characterized by a distinctive bull’s-eye rash, fatigue, headache, and joint pain, Lyme disease requires prompt antibiotic treatment to prevent long-term complications. Other concerning tick-borne illnesses include ehrlichiosis, babesiosis, and Powassan virus, each with potentially serious health consequences if diagnosis is delayed.
Recognizing Warning Signs That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
The symptoms of tick-borne diseases often mimic common illnesses, making them easy to dismiss. Fever, fatigue, muscle aches, headaches, and rashes typically develop within days to weeks after a bite. Some conditions, like Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, can progress rapidly, while others may develop more slowly. The CDC notes that tick-borne disease symptoms vary but often include fever and rash, particularly in the case of RMSF and Lyme disease.
In more severe cases, untreated tick-borne diseases can lead to serious complications including neurological problems, heart issues, and even a condition called tick paralysis. This rare but serious condition is caused by a toxin in tick saliva that can lead to weakness or paralysis, though movement typically returns within 24 hours after tick removal. Alpha-gal syndrome, a recently recognized tick-related food allergy to red meat, represents another potential consequence of certain tick bites.
Prevention and Proper Response to Tick Bites
Taking preventive measures significantly reduces tick bite risk. Wearing long sleeves and pants when outdoors, using DEET-containing repellents on exposed skin, and treating clothing with permethrin provide effective protection. After outdoor activities, conducting thorough body checks helps identify and remove ticks before they can transmit disease. Pay special attention to hidden areas like the scalp, ears, armpits, groin, and behind the knees.
If you discover an attached tick, proper removal technique matters. Use fine-tipped tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin as possible and pull upward with steady pressure. Avoid twisting or jerking, which can cause mouth parts to break off in the skin. After removal, thoroughly clean the bite area and your hands with rubbing alcohol or soap and water. Most importantly, monitor for symptoms in the following weeks and seek medical attention promptly if any develop.